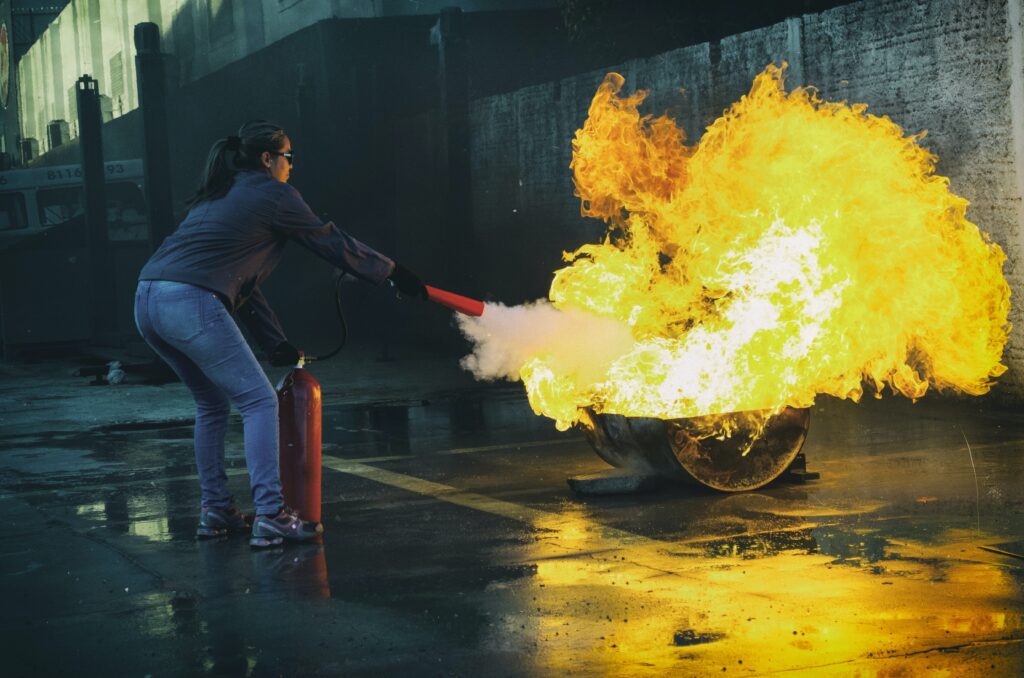
Fires can happen anywhere and anytime and can be extremely dangerous and damaging. It is the worst situation when it comes to emergencies. A proper fire prevention plan is essential for your office, home, or elsewhere.
There are different types of fire, each requiring a specific approach for extinguishment. Understanding the behaviour of various fires is essential to know how to put them best out and prevent further danger.
For a normal person, it is vital to learn the basics of fire safety and become aware of the different types of fires and how they can be extinguished. TrueMedic Ltd believes that fire safety awareness is powerful knowledge, and it’s our job to share what we know.
So let’s discuss the different types of fire and their behaviour and how we can use the right approach to extinguish them.
Types Of Fires That Can Occur

Different types of fire can occur due to other kinds of fuel and oxygen in the environment. Most of us need to be aware of the different types of fire and their behaviour. With proper fire safety training, we can increase our knowledge and awareness. Here are some common types of fires that can occur: [1]
1. Solid Fuel Fire
This type of fire occurs when a solid fuel such as wood or paper is burning. The flames from this type of fire are typically yellow and can be challenging. When putting it out, using an extinguisher designed for this type of fire is essential.
2. Liquid Fuel Fire
If you’ve ever seen a gas or oil burning fire, you’ve seen a liquid fuel fire. This type of fire is usually blue and has the potential to spread quickly. If you encounter this fire, getting to safety as soon as possible is essential. Use an extinguisher designed for liquids when attempting to put it out.
3. Electrical Fire
This type of fire is usually caused by faulty wiring or electrical appliances. The flames from these fires are typically white and difficult to put out. It is vital to cut off the power source as soon as possible and then use an extinguisher specifically designed for electrical fires when attempting to put it out.
Classes Of Fire | A Basic Overview

Fires are classified into four categories or classes, each with unique characteristics and extinguishing methods. Here is a basic overview of the different classes of fire and how they can be extinguished: [2]
1. Class A Fire
This class represents burning flammable solids like wood, paper, cloth, and plastics. Using an extinguisher designed for solids to put out these fires is essential.
2. Class B Fire
This class represents burning flammable liquids such as gasoline, oil, and tar. Many times, these fires require a foam extinguisher to put out. An extinguisher designed explicitly for liquids is essential when putting out these fires to get the best results.
3. Class C Fire
Fires involving flammable gases like natural, propane, and methane can be dangerous. To ensure everyone’s safety, utilizing an extinguisher designed explicitly for gaseous flames is vital when trying to douse them.
4. Class D Fire
If you’ve ever seen a fire in an industrial setting, it was most likely a Class D fire. This class represents burning metals such as sodium, magnesium, and aluminium. When attempting to douse these infernos, it is essential to employ a fire extinguisher specifically designed for metals.
5. Class E Fire
This class represents the burning of electrical appliances and wiring. It is essential to turn off the power source as soon as possible and then use an extinguisher specifically designed for electrical fires to extinguish this type of fire.
6. Class F Fire
Burning cooking oils and fats like vegetable oil, lard, and butter. Using foam or an extinguisher with a cooling agent is best for this type of fire.
The Fire Behaviours That Must Be Considered

Fire has distinct, unique ways of behaving that enable it to spread heat and flames from one area to the next. Heat transmission is accomplished through various objects and principles. As the fire moves, it can ignite new areas with ease.
Here are some ways heat and flames move from one place to another. If you are vigilant about these factors and take appropriate safety measures, you can prevent or at least contain fire emergencies. [3]
1. Radiant Heat
Heat is not merely transferred through contact but is also passed around through electromagnetic waves. This explains why we can sense heat even when an object does not contact us directly. If something gets too close to a flame, it may absorb so much radiation that its temperature rises enough for ignition.
For example, if you put a magnifying glass near paper on a hot day, the sun’s rays will be focused on one spot, and its energy will be amplified. This could set fire to the sheet quickly.
2. Conduction
Heat is transmitted through the collision of atoms that make up various substances. This allows heat to move from one atom to another and eventually travel throughout an entire item. In this way, it moves across solid objects like metal or wood.
3. Convection
Heat can be transferred along with a liquid or gas as they travel. For example, when a fire is lit in a room, the warm air near it will rise and travel throughout the area. This also explains why hot air balloons can move around in the atmosphere.
4. Direct Contact
Heat can travel from one object to another through direct contact. This happens when two items are placed close enough, and the heat travels from one to the other. For example, if a burning candle is placed near a piece of paper, its heat will eventually cause it to ignite.
TrueMedic Ltd provides a Level 1 and Level 2 Award in Fire Safety Training that covers all aspects of fire safety awareness and preparation. Our experts will help you understand these behaviours and provide the tools for effective prevention and preparedness.
For more detailed advice and information, please don’t hesitate to contact us. We are here to help.
FAQs
1. Why is it essential to study fire behaviour?
We can save lives and money by recognising where a wildfire will most likely spread. This vital insight allows decision-makers to strategically place fuel reduction treatments in places that will effectively alter how fire behaves.
2. What is the fire behaviour triangle?
Combustion can only be achieved when three components are present: oxygen, heat, and fuel, forming the fire triangle. Without one of these components, a fire cannot exist. The fire will not remain active if we can prevent just one of these from existing.
3. What is extreme fire behaviour?
Overwhelming flames often accompany severe wildfires, high-speed spreading, crowning and spotting of trees, fire whirls, and intense convection columns. These conditions usually make direct control action impracticable.
References:
[1]https://cpdonline.co.uk/knowledge-base/health-and-safety/the-different-types-of-fires/
[2]https://tutorcare.co.uk/traininghub/fire-safety-awareness-prevention/